Overview
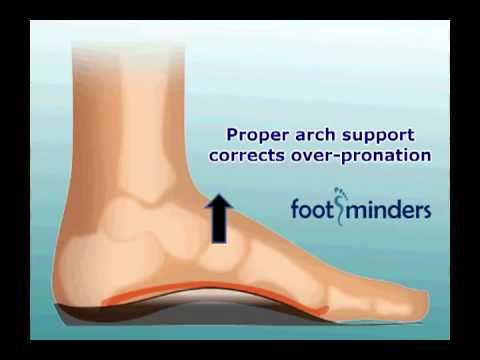
Because young children are unlikely to suspect or identify flat feet on their own, it is a good idea for parents or other adult caregivers to check on this themselves. Besides visual inspection, parents should notice whether a child begins to walk oddly or clumsily, for example on the outer edges of the feet, or to limp, during long walks, and to ask the child whether he or she feels foot pain or fatigue during such walks. Children who complain about calf muscle pains or any other pains around the foot area, may be developing or have flat feet. Pain or discomfort may also develop in the knee joints. A recent randomized controlled trial found no evidence for the efficacy of treatment of flat feet in children either for expensive prescribed orthoses (shoe inserts) or less expensive over-the-counter orthoses.
Causes
Family history, experts say fallen arches can run in families. Weak arch, the arch of the foot may be there when no weight is placed on it, for example, when the person is sitting. But as soon as they stand up the foot flattens (falls) onto the ground. Injury, arthritis, tibialis posterior (ruptured tendon), pregnancy, nervous system or muscle diseases, such as cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, or spina bifida. Tarsal Coalition, the bones of the foot fuse together in an unusual way, resulting in stiff and flat feet. Most commonly diagnosed during childhood. Diabetes. Age and wear and tear, years of using your feet to walk, run, and jump eventually may take its toll. One of the eventual consequences could be fallen arches. The posterior tibial tendon may become weakened after long-term wear a tear. The postario tibial tendon is the main support structure of the arch of our feet. The tendon can become inflamed (tendinitis) after overuse - sometimes it can even become torn. Once the tendon is damaged, the arch shape of the foot may flatten.
Symptoms
Structural problems in your feet like fallen arches can alter your walking pattern, running pattern and cause pain throughout your body. Clear and accurate assessment of the mechanics of your lower limbs is key to understanding the profound effect that subtle faults in your foot, ankle, knee and hip alignment can cause.
Diagnosis
An examination of the foot is enough for the health care provider to diagnose flat foot. However, the cause must be determined. If an arch develops when the patient stands on his or her toes, the flat foot is called flexible and no treatment or further work-up is necessary. If there is pain associated with the foot or if the arch does not develop with toe-standing, x-rays are necessary. If a tarsal coalition is suspected, a CT scan is often ordered. If a posterior tibial tendon injury is suspected, your health care provider may recommend an MRI.
What causes pes planus?
Non Surgical Treatment
Traditionally, running shoes have contained extra padding to support the feet in general and fallen arches in particular. Orthopedists may prescribe orthotics for people with flat feet. More recently, however, the argument has arisen for shoes that provide a more minimal amount of padding and support for the feet. The idea here is that the feet will strengthen themselves. Since there are multiple options, anyone with flat feet or fallen arches would do well to explore them all.
Surgical Treatment

Surgical procedures for flat feet vary depending on the root cause of the condition. Surgical correction to control pronation may include bone implants or Achilles tendon lengthening. Tendon transfer, which is a procedure to re-attach a tendon to another area of bone, may also be used to reduce pronation and improve foot function.
Prevention
Flat feet or Fallen Arches cannot be prevented due to congenital of nature or from underlying disease process; however, painful symptoms and future pathology from Flat Feet or Fallen Arches may be prevented by the following. Continue to wear your orthotics for work and exercise to provide stability and maintain function of your feet. Footwear. Continue to wear supportive shoes to maximise the function of your orthotic and prevent excessive movement of the joints in your feet.

Because young children are unlikely to suspect or identify flat feet on their own, it is a good idea for parents or other adult caregivers to check on this themselves. Besides visual inspection, parents should notice whether a child begins to walk oddly or clumsily, for example on the outer edges of the feet, or to limp, during long walks, and to ask the child whether he or she feels foot pain or fatigue during such walks. Children who complain about calf muscle pains or any other pains around the foot area, may be developing or have flat feet. Pain or discomfort may also develop in the knee joints. A recent randomized controlled trial found no evidence for the efficacy of treatment of flat feet in children either for expensive prescribed orthoses (shoe inserts) or less expensive over-the-counter orthoses.
Causes
Family history, experts say fallen arches can run in families. Weak arch, the arch of the foot may be there when no weight is placed on it, for example, when the person is sitting. But as soon as they stand up the foot flattens (falls) onto the ground. Injury, arthritis, tibialis posterior (ruptured tendon), pregnancy, nervous system or muscle diseases, such as cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, or spina bifida. Tarsal Coalition, the bones of the foot fuse together in an unusual way, resulting in stiff and flat feet. Most commonly diagnosed during childhood. Diabetes. Age and wear and tear, years of using your feet to walk, run, and jump eventually may take its toll. One of the eventual consequences could be fallen arches. The posterior tibial tendon may become weakened after long-term wear a tear. The postario tibial tendon is the main support structure of the arch of our feet. The tendon can become inflamed (tendinitis) after overuse - sometimes it can even become torn. Once the tendon is damaged, the arch shape of the foot may flatten.
Symptoms
Structural problems in your feet like fallen arches can alter your walking pattern, running pattern and cause pain throughout your body. Clear and accurate assessment of the mechanics of your lower limbs is key to understanding the profound effect that subtle faults in your foot, ankle, knee and hip alignment can cause.
Diagnosis
An examination of the foot is enough for the health care provider to diagnose flat foot. However, the cause must be determined. If an arch develops when the patient stands on his or her toes, the flat foot is called flexible and no treatment or further work-up is necessary. If there is pain associated with the foot or if the arch does not develop with toe-standing, x-rays are necessary. If a tarsal coalition is suspected, a CT scan is often ordered. If a posterior tibial tendon injury is suspected, your health care provider may recommend an MRI.
What causes pes planus?
Non Surgical Treatment
Traditionally, running shoes have contained extra padding to support the feet in general and fallen arches in particular. Orthopedists may prescribe orthotics for people with flat feet. More recently, however, the argument has arisen for shoes that provide a more minimal amount of padding and support for the feet. The idea here is that the feet will strengthen themselves. Since there are multiple options, anyone with flat feet or fallen arches would do well to explore them all.
Surgical Treatment

Surgical procedures for flat feet vary depending on the root cause of the condition. Surgical correction to control pronation may include bone implants or Achilles tendon lengthening. Tendon transfer, which is a procedure to re-attach a tendon to another area of bone, may also be used to reduce pronation and improve foot function.
Prevention
Flat feet or Fallen Arches cannot be prevented due to congenital of nature or from underlying disease process; however, painful symptoms and future pathology from Flat Feet or Fallen Arches may be prevented by the following. Continue to wear your orthotics for work and exercise to provide stability and maintain function of your feet. Footwear. Continue to wear supportive shoes to maximise the function of your orthotic and prevent excessive movement of the joints in your feet.



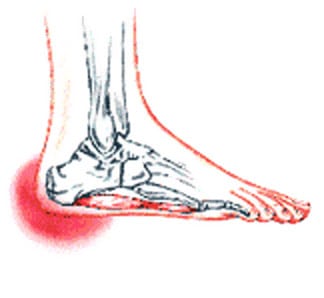
 During certain activities, particularly weight-bearing activities (e.g. walking or running) a compressive force, is sometimes placed on the interdigital nerves and surrounding soft tissue, between the metatarsal bones (this is often the case with tight fitting shoes or in patients with flat feet). If this force is repetitive enough and beyond what the nerve and soft tissue can withstand, swelling to the nerve and soft tissue may occur. This may result in pain, tenderness, pins and needles or numbness in the forefoot or toes. When this happens, the condition is known as a Morton's neuroma.
During certain activities, particularly weight-bearing activities (e.g. walking or running) a compressive force, is sometimes placed on the interdigital nerves and surrounding soft tissue, between the metatarsal bones (this is often the case with tight fitting shoes or in patients with flat feet). If this force is repetitive enough and beyond what the nerve and soft tissue can withstand, swelling to the nerve and soft tissue may occur. This may result in pain, tenderness, pins and needles or numbness in the forefoot or toes. When this happens, the condition is known as a Morton's neuroma.





 Symptoms
Symptoms Overview
Overview Symptoms
Symptoms RSS Feed
RSS Feed
